Sector Analysis: Understanding Market Performance by Industry
Introduction
Sector Analysis is a crucial part of investment research that evaluates the performance of different market sectors. Investors use sector analysis to identify leading industries, sector rotations, and investment opportunities in the stock market.
What is Sector Analysis?
Sector analysis involves studying the economic, financial, and performance trends of specific market sectors. Each sector consists of companies operating in a similar industry, such as Technology, Healthcare, Energy, or Financials.
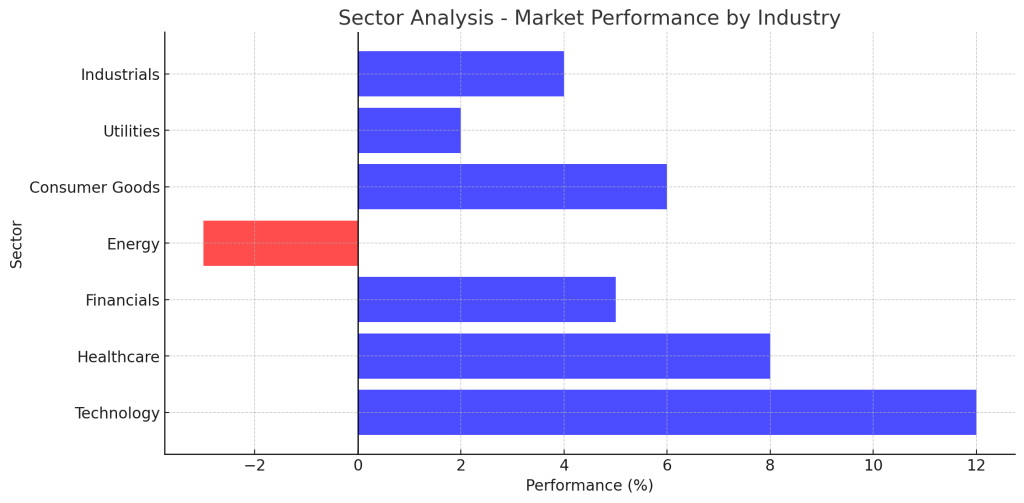
By analyzing sector performance, investors can determine which industries are outperforming or underperforming, helping them make informed investment decisions.
Key Components of Sector Analysis
- Sector Performance: Evaluates the percentage change in sector indices over time.
- Economic Impact: Determines how macroeconomic factors affect different sectors.
- Market Trends: Identifies emerging opportunities and risks within industries.
- Sector Rotation Strategy: Tracks money flow between sectors based on economic cycles.
How to Conduct Sector Analysis
1. Identifying Strong and Weak Sectors
- Compare sector indices to benchmark indices like the S&P 500.
- Analyze historical performance and recent trends.
2. Economic Cycle and Sector Rotation
- Early Cycle Sectors: Technology, Financials – thrive in economic recovery.
- Mid-Cycle Sectors: Industrials, Consumer Discretionary – grow as the economy strengthens.
- Late Cycle Sectors: Energy, Materials – perform well when inflation rises.
- Defensive Sectors: Healthcare, Utilities – outperform during economic downturns.
3. Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Fundamental Analysis: Reviews financial health, earnings, and growth potential.
- Technical Analysis: Uses price trends, moving averages, and RSI to assess sector strength.
Example of Sector Analysis in Action
- Suppose Technology and Healthcare sectors are outperforming the market.
- Investors may shift funds into these sectors to capture growth opportunities.
- If the economy slows, money may rotate into defensive sectors like Utilities.
Advantages
- Identifies Market Leaders: Helps investors focus on strong-performing sectors.
- Enhances Portfolio Diversification: Reduces risk by investing across multiple sectors.
- Improves Investment Timing: Guides investors on when to enter or exit certain industries.
Limitations
- Sector Performance Can Change Rapidly: Market conditions and economic cycles shift frequently.
- Not a Standalone Strategy: Works best when combined with stock selection and macroeconomic analysis.
Conclusion
Sector Analysis is an essential tool for investors seeking to understand market dynamics and optimize portfolio allocation. By analyzing sector performance and economic trends, traders can make strategic investment decisions and capitalize on market opportunities.